Chapter 1: "Wait, Is SEO Dead in 2019 or Not?"
Chapter 2: The History of SEO and Organic Search
Chapter 3: The Rise of Mobile Search
Chapter 4: Google RankBrain Changes the Game
Chapter 5: What You Need to Know About Voice Search
Chapter 6: SEO Strategies & Tactics That Still Matter
Chapter 7: SEO Strategies & Tactics That Don’t Matter Anymore
Chapter 8: The Relationship Between High-Quality Content & SEO
Chapter 1: "Wait, Is SEO Dead in 2019 or Not?"
About this time every year, as the iced lattes give way to pumpkin spice and eggnog overwhelm, Twitter blows up with the perennial cliché:
"Is SEO dead?"
This is then followed by the inevitable argument on both sides is that yes, SEO is dead, and life as we know it is over. And, as if on cue, the flame wars quickly escalate, ebbing and flowing with contrary arguments.
Today, however, we are taking a break from this regularly scheduled programming of hand-wringing over search engine optimization to proclaim in the immortal words of Mark Twain, "The death of SEO is greatly exaggerated."
In 2016 companies spent 65.26 billion dollars on SEO tactics. That number swelled to 72 billion in 2018. And by 2020 it's estimated that companies will spend a whopping 79.27 billion dollars on search engine optimization.
But what does that mean for your marketing strategies? Why do so many insist that SEO is over, as we know it?
Let's say that you had the good fortune of owning a website that has a keyword listed as the first result on Google. On average, you're getting 32.5% of all of the traffic for that keyword.
Given that keywords can be considered high-volume and extremely relevant to some users, there may be a little money behind those keyword for you. Even if you don't have a #1 Google listing, 51 percent of all website traffic comes from organic search, which means it should have a pretty big impact on your bottom line.
As a matter of fact, 40% of revenue is captured by organic traffic.
Think about that for a moment -- 40% of the dollars that hit your bank account should come from some type of organic search result. If not, your website is leaking customers.
Now we start to see why the death of SEO is so important -- if SEO does die, there's a lot of money it’s taking with it to the grave.
Let's talk about the fundamental truth of improving your website for search. If something were to change with SEO and all of a sudden 40% of your revenue started going to some other company, what's the first thing that you would do?
Maybe claim that the death of SEO is upon us? Or, would we just start paying Google Ads for all of the traffic that we lost from organic sources and give them more money than the $9.4 billion they're making per quarter right now?
Taking all this into account, I think we can comfortably say that SEO is alive and kicking.
But we have to admit that all of these cries that the SEO sky is falling aren't without merit. As search engines have evolved -- both proactively and in response to marketers -- SEO has changed a lot. And many of the tried-and-true tactics of yesteryear that used to reliably yield results aren't worth the effort anymore.
This is a pattern that will, undoubtedly, continue.
So, in order to stay ahead and be ready for what's next, marketers need to understand how we got to this point and what's changed already.
Chapter 2: The History of SEO & Organic Search
How We Got Here
How did we get to a place where we need to contemplate the mortality of SEO? To answer that question, let's rewind back to 2010.
On May 25, 2010, a website called, "SEO is dead" hit the hot sheets. The author posted it as a drunken rant about the supposed death of SEO by a supposed SEO expert.
In internet years, 18 years ago was an eternity. The state of Google at that time was nowhere near the capability of what Google is today.
Back in the golden age of search, a lot of black hat SEOs -- meaning SEO specialists who would try to game a search engine -- used shady techniques like adding keyword-rich text at the bottom of a page and then making the text of the page the same color as the background. You really couldn't see it, but the search engines would find the text on the page anyway. The sad part of that story is that it used to work.
Another tool in their bag of tricks was to buy backlinks from nefarious sources and point hundreds, if not thousands, of backlinks to it. Again, strike two for Google because the algorithm couldn't understand that these were unnatural links.
The Birth of Modern SEO
Google knew the fact that these shortcuts worked -- and were widely used by marketers to make their content rank higher -- was a big problem.
So, being the forward-thinking engineers they are, they wrote code to try to circumvent these ne'er-do-wells and their sneaky strategies. All of a sudden, we had algorithms named after cute, furry animals like pandas and penguins, and some feathered friends like hummingbirds.

When these black hat techniques stopped working, SEO specialists and marketers had to a find a way to rank their websites using different techniques. In one sense, this was the very first example of the death of SEO, and the resurgence of something completely new and exciting.
The fundamental truth about the death of SEO is that it does die and reincarnate in different forms.
We're going to try to explain what these iterations are and what we do about them every time we see a massive change. Needless to say, those of us who live and breathe SEO live in a constant state of change and struggle.
You could spend months working on an SEO feature only to wake up in the morning, grab your fresh cup of espresso, and find out that all of those months of hard work evaporated like the money in my bank account every weekend.
So, we slurp down our coffee, crank open our weathered keyboards, and start keyword researching again.
We beat ourselves over the head with a hammer and continue to work on valuable content that’s search engine optimized, because the efforts -- when done correctly -- are dramatic.
Chapter 3: The Rise of Mobile Search
What's the first thing that you do after you get up in the morning? Maybe you reach over your nightstand and grab your phone to start browsing the morning’s Facebook posts. (Psh, I never do that.)
In May of 2015, mobile searches overtook desktop on Google. Few websites on the internet were ready for mobile search back then. Google took notice and started altering the algorithms to focus on delivering the best experience on the smallest device possible.
In many ways, SEO did die at this point because now we had to think about websites from a mobile usability standpoint -- and so, the death knell rang for widescreen widths and heralded the birth of mobile responsive design.
“What Is Mobile Responsive Design?"
Websites that follow a mobile responsive approach to design have layouts and content that resize and adapt automatically to the screen it's being viewed on. Generally speaking, there are four screen sizes considered by mobile responsive web designers: desktop, laptop, handheld tablet, and smartphone.
This avoids the old school problem of having to pinch and zoom to read content on websites in a smaller format, or having to publish and maintain a completely separate mobile website experience.
The responsive viewports had to change. The screen resolutions we use to build websites got much smaller, and we had to account for users that experienced websites across multiple devices in a single session. Meaning, they sat down at their desktop to search for something and then picked up that search on their mobile device.
Or, perhaps they began an online shopping excursion on their mobile device, but didn't check out until later on their desktop computer.
This behavior signaled several things to organic search engines.
Most of all, online searchers were primarily mobile nowadays, and it would become much more important for them to display relevant information on smaller devices.
However, given that mobile device processors and memory are not as robust as their desktop and laptop counterparts, marketers would need to create web pages as light as possible, in order to deliver an optimized experience that wouldn't frustrate their users.
Enter Stage Left, Mobile-First Indexing
If we fast forward to August 2018, Google officially launched the core algorithm called mobile-first indexing. Marketers collectively freaked out -- as we are wont to do -- because this meant the mobile version of a website would primarily be used to gather keywords and assess a site for ranking, rather than the desktop version.
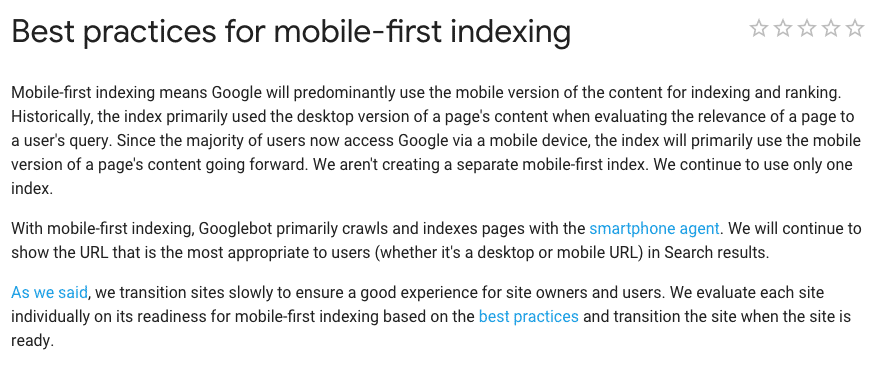
Best practices, outlined by Google.
A quick pulse check shows us how strong mobile search’s vital statistics are. It’s growing at a 15% year-over-year rate, and accounted for 96% of Google searches in the last quarter of 2017
They also added another ranking factor that tests for mobile page speed. The speed of your website on different devices helps Google determine what position to list you on the search engine. So, the trinity of SEO has now become speed, relevancy, and mobile responsiveness.
So, again, SEO died a little death in this moment. Or, at least an older, more desktop-focused version of it did.
Chapter 4: Google RankBrain Changes the Game
Of course, the rise of mobile is only one part of the story. Another critical factor in how SEO continues to die and be reborn in new ways is the significance of more recent Google algorithm updates.
Google really is a living ecosystem of digital connections trying to make sense of the global internet, all while trying to deliver more relevant results to search queries from users, faster.
That's a tall order, given how much device preferences and user behavior have changed drastically in just the past few years. (We'll talk about what exactly has changed with user behavior in the next chapter.)
In 2013, semantic search arrives with the Google Hummingbird update. Then, in 2015, everyone lost their minds over what many called Mobilegeddon -- a release of a "mobile-friendly" algorithm change.
Later that year, Google confirmed the existence of RankBrain.
What Is Google RankBrain?

Google RankBrain is an artificial intelligence program used to help process Google search queries -- and it performs better than humans at delivering the best results. More simply, Google RankBrain's new artificial intelligence looks for signals of human interaction with websites and ranks those sites accordingly.
These signals can take many different shapes and forms -- click-throughs, bounce rates, dwell time, and "pogo-sticking."
"What's pogo-sticking?"
You know when you search for something and Google gives you an index of pages to look for? You click on an entry -- let's say the second or third in the search engine results page (SERP) -- land on a page and notice it’s not what you were looking for. So, you click back to Google, find another entry, click on that, and then you click back again.
When you do that two or three times, you're pogo-sticking.
Now, let's say that one of those entries that you hit was a really valuable post that answered the relevant question you searched for. Maybe you bookmarked it, and you definitely spend some time on that page -- maybe three or four minutes. (That's the hallmark of a site page with a high "dwell time," which literally means how long someone spends on a page.)
Google uses those signals to say, "Hey, this user found a relevant answer and they stayed on the page and got some value from it."
In today's world, that's how you rank higher than your competitors.
Essentially, your content has to be awesome and the most useful to the visitor. If you haven't figured out how to create content that's absurdly useful and of high-quality, no amount of SEO expertise -- technical or otherwise -- will save your content from oblivion.
Chapter 5: What You Need to Know About Voice Search
In addition to high-quality content becoming an absolute necessity if you want to rank well in search results, the way people now search for has fundamentally changed, which IMPACT Director of Web and Interactive Content Liz Murphy summarized during the first three minutes of her IMPACT Live '18 talk:
Watch the first three minutes of this video to learn about the rise of voice search.
The rise of voice search on mobile devices is another great example of one area of SEO dying and another one surging.
Voice Search Statistics You Need to Know
Now, of course there are those who say voice search really isn’t a thing, for whatever reason -- maybe they think it's a passing fad, or they're still clinging desperately to their laser disc collection, waiting for a comeback.
If you are a marketer who still isn't too keen on the whole voice search thing, here are some statistics that may change your mind:
- About 30% of all searches will be done without a screen by 2020. (Gartner)
- 52% of people keep their voice-activated speakers in their living rooms. 25% keep them in their bedrooms, while 22% keep them in their kitchens. (Google)
- 35.6 million Americans used a voice-activated assistant device at least once a month in 2017 (eMarketer)—a year-over-year increase of 128.9%. (WordStream)
- 1 in 4 shoppers used voice assistants in their holiday shopping during the 2017 season. (CTA)
- 72% of people who own voice-activated speakers say that their devices are used as part of their daily routines. (Google)
- Mobile voice-related searches are 3X more likely to be local-based than text-related searches. (Search Engine Watch)
- 65% of people who own an Amazon Echo or Google Home can’t imagine to going back to the days before they had a smart speaker. (GeoMarketing)
- 41% of people who own a voice-activated speaker say it feels like talking to a friend or another person. (Google)
The traditional search engine user experience of 10 entries in blue text that we’re familiar with is giving way to knowledge panels, local pack entries, Google Map listings, carousels, and an array of modern SERP features.
While these features are difficult for content marketers to code, they are highly useful to those seeking results. Moreover, all of these new SERP features are found on both mobile and desktops devices -- which means marketers need to get on the ball.
Still not convinced? Look around you.
Pay attention to your friends and family’s search habits on mobile devices. I've caught myself asking Google or Alexa for an answer when I feel lazy and don't want to sit down at a desk and search for something, or pick up the phone and order a pizza.
Convenience is a powerful motivator -- and something to pay attention to when you see similar behavior patterns in other people.
It seems that we're not the only ones searching. Voice searches have dramatically increased recently, not only on platforms such as Google, but also on Alexa, Bing, Yahoo, and a host of other voice-capable devices.
The technology is very new and difficult to implement, but forward-looking companies are taking advantage of voice search. The trends show us that traditional organic search is morphing into more natural ways of communicating with the machines.
How to Optimize Your Content for Voice Search
Given the rise of voice search, and the powerful metrics behind its meteoric rise, what can you do today to prepare for the eventual flood of voice traffic? WordStream does a great job of breaking down an easy roadmap for you to follow:
Focus on User Intent
First and foremost, think about your users when creating content and presenting it on a page. Is it what they would want to find? Is it as helpful as possible and laid out in a way that doesn't make them want to claw their eyes out? The more you solve for the user by going out of your way to anticipate their questions, to answer those questions clearly, and to make those answers easy to find, the better off you'll be.
Target Long-Tail Keywords
The more specific the search strings you go after, the better chance you'll have to rank and create content that's more in-line with the intent of the searcher. (As the rise of voice search has shown us, searcher queries are becoming longer and more complex. In fact, 70% of all search traffic falls into the long-tail category.)
Don't Optimize for a Specific Search Engine
Google tends to dominate the conversation when marketers talk about SEO. To the point where search engines like Bing and Yahoo! are treated like more of a punchline.

Unless you have a very compelling reason to optimize your content for a specific search engine globally -- for example, you exclusively target Apple users, and Siri is powered by Bing as its primary search engine -- there is no reason to focus on anything other than creating high-quality, relevant content that's served up on a website that looks nice on multiple devices and is lightweight, from a coding perspective.
Use Schema Markup
This part is a little technical, and a job for the technical SEO experts at your organization. Using schema markup language, website owners can give additional information about a particular website to search engines, without it being displayed for the user on a site page. This is a good thing, and you should tell your developers and technical SEO specialists to use schema to help Google better understand what your website is all about.
Optimize for "Near Me" Searches
One of the fastest growing search trends is users searching for stuff "near me."
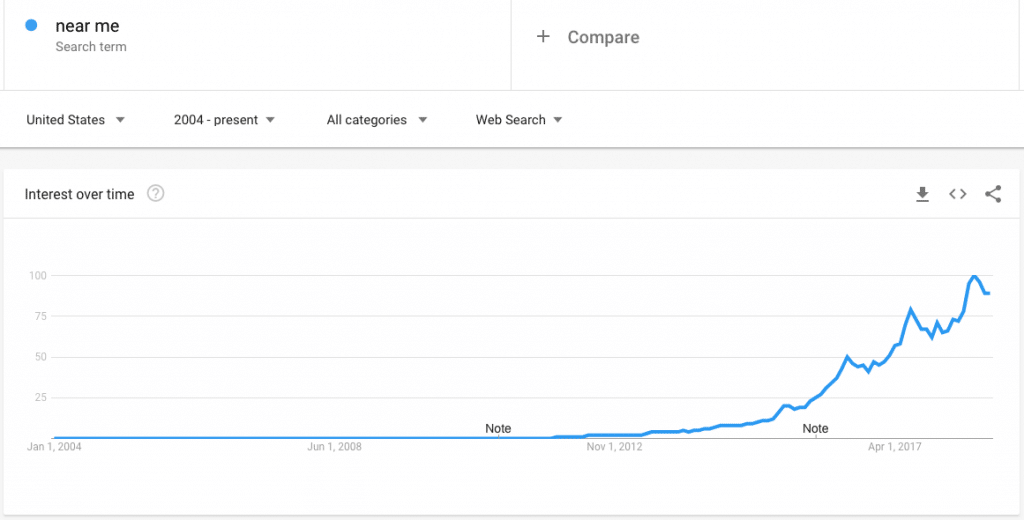
Google Trends reporting on "near me" searches, 2004 through to the present.
This should come as no surprise, as consumers are becoming more reliant upon their mobile devices and voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Home to help them find restaurants, gas stations, grocery stores, and other businesses or places near them.
Google Ads has a few ways you can capitalize on this -- if it makes sense for your business; it may not -- through location extensions and local search ads in Google Maps.
Make the Most of Your Google My Business Listing
One of the best online tools for businesses that is criminally underutilized is Google My Business (GMB), which allows you to manage your online presence in Google Search and Maps. Often, you'll see this information populate in what's called a "knowledge panel" in your search results:

Chapter 6: SEO Strategies & Tactics That Still Matter
Given that there are somewhere between 200 to 500 rank factors that we think we know about in Google, what is a marketer to do to keep up with these changes? Which SEO strategies and tactics continue to work perennially that perhaps move the needle?
Technical SEO Basics for Marketers
Fortunately, the infrastructure of the web doesn’t change all that much. DNS, TCP/IP, and server operating systems like Linux, Ngix, and IIS are the immortal pillars of the internet.
I know that sounded like a lot of mumbo jumbo to most marketers, but here's the deal -- if your server isn’t healthy, no amount of SEO magic will place your content in front your ideal users.
That means the first thing you need to do to nail SEO in 2019 is stay in the loop with your web team to make sure nothing goes awry and learn more about the technical SEO factors that influence your website's search rankings -- no matter how unsexy it may seem to "look under the hood" at first.
If you're already nailing this, great! You're a step ahead of the crowd, because technical SEO seems to be the part of the equation that never goes out of style.
Web servers are a perfect example -- they're the scorned children of SEO, and server issues are commonly overlooked by small businesses. Neglecting technical SEO is a great way to kill your keyword density and competitive advantages. The teeming digital connections beneath your website's core is the micro biome that keeps your website healthy.
The Trinity of SEO
When we run a technical SEO report on a domain, we use a framework called the "Trinity of SEO," which is a blend of technical SEO and standard SEO practices. It keeps the overwhelming workload manageable (to a degree) and narrows the project down to the optimizations that provide the best results.
Pillar #1: Page Speed
How well your website ranks now lives and dies by page speed, or how quickly your site pages load. While there are a lot of ways you can fix this through more superficial means -- for example, compressing and optimizing images -- most companies look at their server or hosting company as an afterthought, when assessing their page speed.
This is a huge mistake. Search engines pay very close attention to the technical components and the responsiveness of a website at this level. So, again, talk to your web team. Find out what you can do "under the hood" to make your website as lean as possible.
Pillar #2: SSL/TLS
The second part of the trinity is security. SSL certificates became important back in 2014, when Google announced that whether or not a site was HTTPS instead of HTTP would become a rank factor, as it is a clear signal that a user's data is protected on that site.
Today, not having one will get you a big red flag that your site is not secure by this standard in Google. More importantly, your website visitors expect your site to be secure if you want to gain their trust (and business).
Pillar #3: 80/20 Prioritization
What are the 20% of things that you can do today, to improve your results by 80%? The prioritization that comes out of the answer to this question makes up the third and final part of the trinity.
Basic website audits surface problems that can be easily dealt with that provide immediate improvements when done correctly. Heck, not even done correctly, just done.
Boiling it down to simple basics, make sure that your website is as fast as it can be:
- As we discussed already, start with your server -- this is where you'll see the biggest potential for site speed improvements.
- Next, work on your on-page SEO, including your website's database and maybe your images.
- Still missing a security certificate? The time was four years ago to implement it, so get on it.
- I'm going to go out on a limb and say that the images on your website are too big. Virtually 99% of the website audits we run show problems with under-optimized images. Start with a global image optimization, and watch what happens to your keyword densities.
These strategies and tactics, while seemingly simple, provide the biggest SEO gains in a large majority of the websites we test.
Go for "Position Zero" with Featured Snippets
OK, that's enough technical stuff for now. Let's dive into something that I think a lot of marketers will have a lot fun sinking their teeth into.
It used to be that ranking #1 was the ultimate goal of every marketer -- which is why so many marketing agencies promise to get you to #1 on the "front page of Google" by tomorrow. That's changed with the advent of "featured snippets" by Google.
What Do Featured Snippets Look Like?
Featured snippets come in a lot of different shapes and forms, but they now reside in what's called "position zero" in search rankings, above any other content that may be displayed:
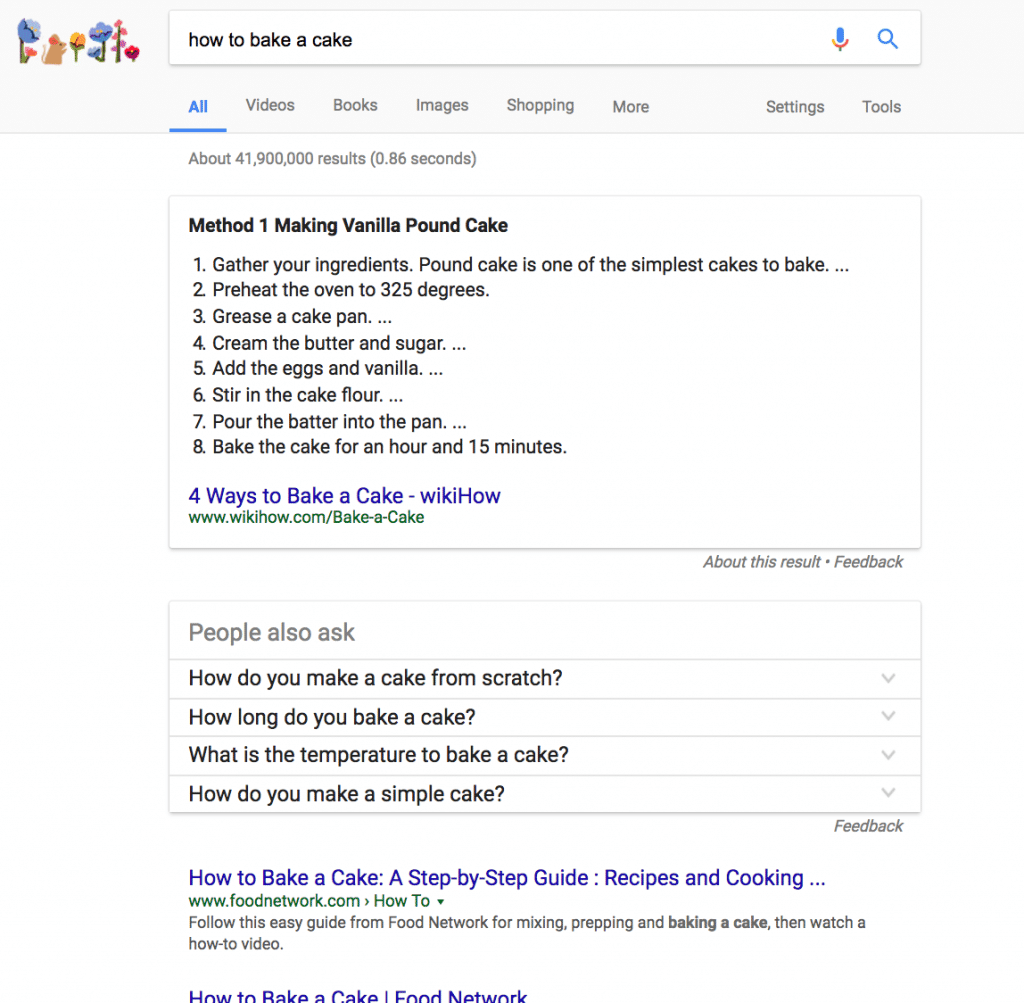
Example 1
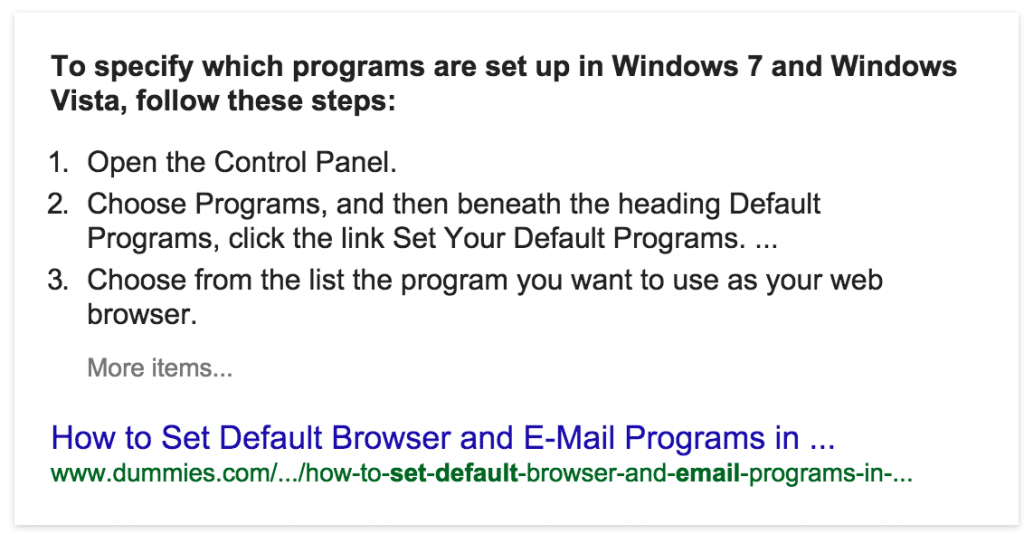
Example 2
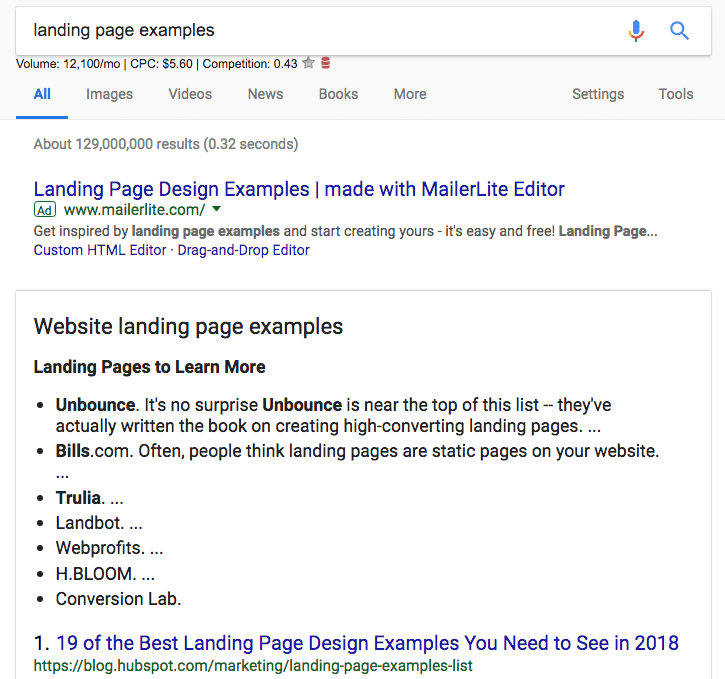
Example 3
With featured snippets, searchers for some -- not all -- search queries will get a sneak preview of the most relevant content option, as determined by Google.
That's why you may have noticed some articles you've been perusing now have some version of this nested within the first third:
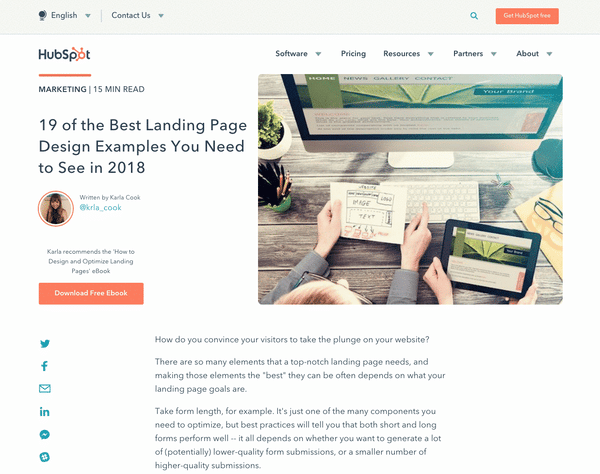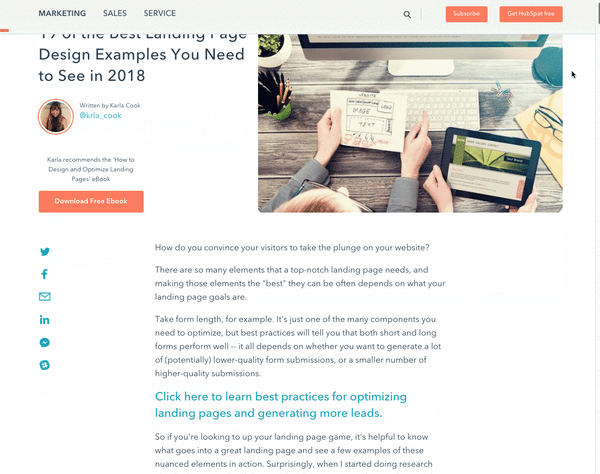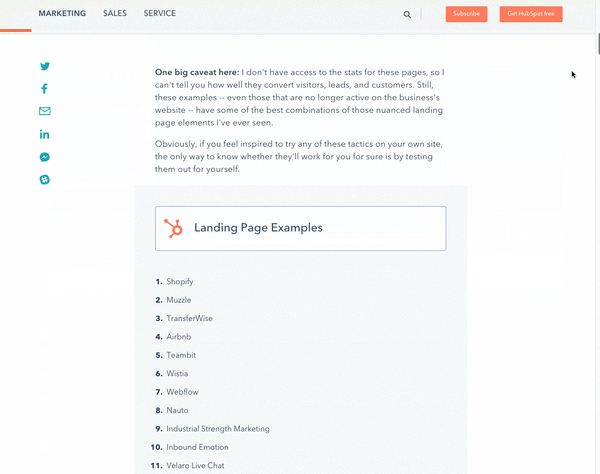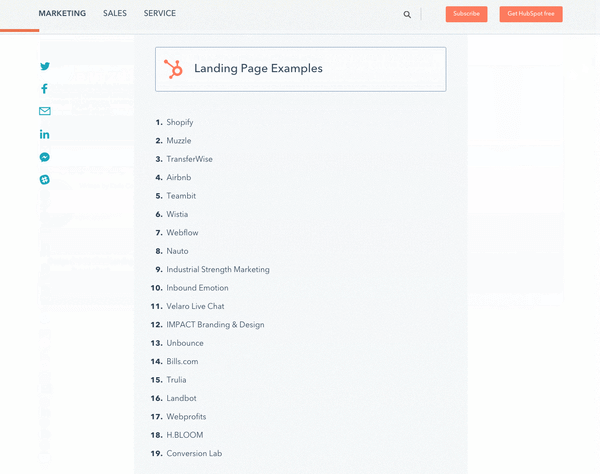
What You Need to Know About Featured Snippets
At IMPACT Live '18, IMPACT's VP of Marketing Kathleen Booth discussed featured snippets at length, including why owning featured snippets is so important, tactics on how to dominate position zero, and what you can expect to see in future, as search continues to evolve.
I'm willing to bet many, many dollars that featured snippets aren't going anywhere. So, take 10(ish) minutes to watch this video -- it will give you loads of juicy SEO stuff to do right now.
Chapter 7: SEO Strategies & Tactics That Don’t Matter Anymore
Now that we know what to focus on let's talk about things that have gone out of favor.
I'm going to start with a wild guess that your inbox has an email from an SEO firm telling you that backlinks are the #1 rank factor, and that your website sucks because you don't have any. Oh, and they’ll sell you some since, you know, they own them all.
Choose Relevancy Over Backlinks
Backlinks are still very, very important to SEO. But the mistake most marketers need to stop making in 2019 is prioritizing backlinking over relevancy.
Speaking of which, I have a quick question for you on content relevancy:
Whether your content is 300 words or 5,000 words long, is it relevant to the end-user?
I ask because Google will display a 300-word blog post if it's a better answer to the user's search term than the 5,000-word essay on a keyword that the user isn't really interested in. The lesson here is to solve the user's problem with your content.
To that end, my challenge to you is to stop focusing so much on the hard to get backlinks that most websites won’t give to you anyway and start focusing more on the quality of content you're producing. If you don't believe me, I have a another question for you.
How many emails have you gotten this month from someone saying:
“Hey, I've written an article for your space and it would be great on your website. Would you mind posting it for us with a link back to ours?”
Please. Make. It. Stop.
If you write amazing content, the content get backlinks on its own merit. This makes your day much easier. Not only that, you'll sleep better at night not worrying about the fact that you’ve got some overseas company trying to prop up your website by throwing really bad quality links at it.
Say a Final Goodbye to Keyword Stuffing
Another strategy that doesn't work anymore is keyword stuffing. Yes, some of you out there still think this is a good idea... for some reason. It's fine -- and necessary -- to have your keywords in critical areas of your page like the title, meta-descriptions, H1s, and -- to a lesser degree -- H2s.
But repeating the same keyword over and over on a page will get you a penalized. So, stop it.
In fact, it's best to put to bed all of those gaming-the-system strategies, in which you spend most of your time and energy trying to outsmart the machines.
The hard truth is that our great Google overlords are smarter than we are.
So, even if you're able to outsmart them in the short-term, they'll figure out what you're doing down the line -- as they've done many times before -- and you'll be sorry you wasted all of that time on band-aid solutions that were never going to last.
Chapter 8: The Relationship Between High-Quality Content and SEO
We've talked a lot about the importance of creating high-quality, relevant content, if you want your content and your website to rank well in search results.
We've also written a ton on how to create the wonderful, high-quality content that will bring all the boys to the yard:
- The Exact Content You Need to Achieve 6 of Your Biggest Marketing Goals
- The 3 Worst Content Sins (& How to Fix Them)
- How to Write Marketing Copy That Makes People Feel Good
- The 2 Blogging Tips That Will Solve 99% of Your Content Problems
- How to Create Marketing Content Your Sales Team Will Love
- How I Got My Entire Team to Create Content -- Without a Fight!
- How Quality Content Fueled Growth at Unbounce Ft. Oli Gardner
But let's say you've followed all of our advice and written the most beautiful piece of content you've ever written. It perfectly matches the user's search query. It's perfectly relevant to what they're looking for -- but what on-page factors influence a higher rank on Google?
How Google Knows Your Content Is Relevant
First, let's start by reflecting on our own behavior.
When we find a piece of content online that's relevant, we click on that entry within the search result. We read the headline of the text which typically has the keyword in it and piques our interest enough to read first sentence of the text.
We engage with the content and read further down the page and increase the dwell time -- again, the time a user spends on a page -- which Google considers a signal of high-quality content. On average, the first result from a Google Search has a dwell time of three minutes and 11 seconds!
As Google spies on our interaction with the page, it probably noticed that we didn't bounce back to the search entries and click on something else. If you can make that happen and the content is valuable to the users, you'll win.
That's as simple as this can be. But I didn’t say it was easy... just simple.
The Different Flavors of High-Quality Content
High-quality can mean several things. Let’s say you search for a zip code in a nearby city. A long winded blog post isn’t necessary. A simple list of the zip codes is the best answer, like so:

That zip code list is generated by Google. It shows up directly underneath the search bar, and isn’t an organic entry.
The first organic entry isn’t a blog post either. It’s an app-like website that lets you search for zip codes six ways to Timbuktu, and it's relevant and highly useful:

Depending on what information someone is looking for, Google may serve up the results in a way that requires zero navigation to your site (as in the first zip codes example), or it'll pull a different result entirely, because it is, in fact, the most useful "content" to solve someone's Clarksville, Tennessee-specific problem.
Here's another example -- the "most relevant" answer for "apple pie recipe":
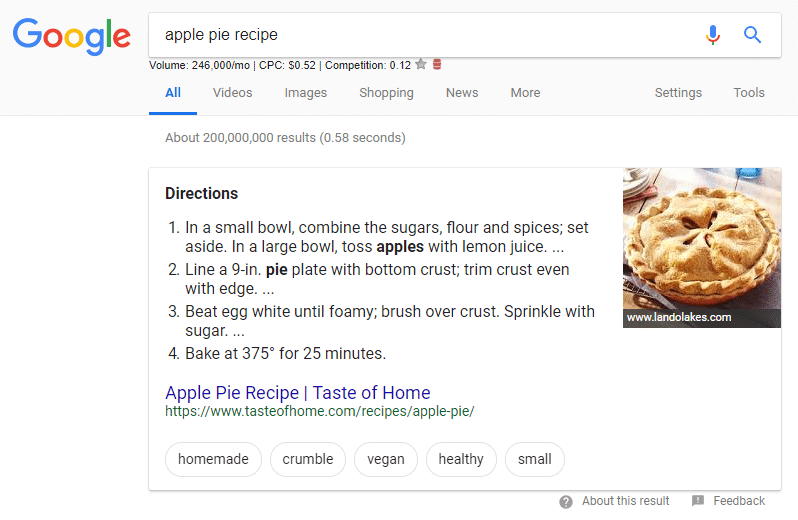
There are a lot of different apple pie recipes out there on the internet, but why does Taste of Home take the cake -- er, pie -- in this case? Because they served this deliciously sweet answer wrapped up in freshly baked schema markup that satisfies our craving. (Yes, it’s in the oven right now. I knew you’d ask.)
So, we start to see that written content isn’t necessarily the king or queen on its own.
Relevant, useful, and authoritative links win more top-ranking slots than ever before, especially if they understand and leverage some of the "under the hood" technical SEO strategies that will push that high-quality content to the top.
Chapter 9: Top Free (& Almost Free) SEO Tools
How do you spot changes in search features? Where can you go to diagnose the inner recesses of your website quickly?
Enter the world of technical SEO tools. While this won't be an exhaustive list, here are software tools the technical SEO community relies on to gather timely information and solve difficult problems. As a digital marketer, any one of these tools on its own will give you an advantage over competitors that aren’t using them.
1. Google Analytics
Google Analytics is the best kept secret in digital marketing. Sure, you know about it, but did you know it’s the best deal you’ll ever find? It’s scalable enough to track metrics for a Fortune 500 company, all the way down to Suzie’s digital lemonade stand.
And you can’t beat the price -- free.

Customizing Google Analytics isn’t too difficult, and if you get stuck, there are hundreds of free and paid courses that’ll teach you the platform quickly.
It's also great "out of the box," but if you want a replacement for your MarTech software (which Google Analytics can do) you’ll need an experienced consultant or firm that specializes in conversion tracking within the platform.
When paired with the tools below, it’s a one-two punch of technical SEO data and marketing metrics.
Why It's Awesome
-
You can use your existing Google account to sign up.
-
Easy integration to any website or CMS.
-
Customizable goals, views, and segments.
-
Integrates with Google Tag Manager to track scroll depth, video metrics, button clicks, and much more.
-
Allows for cross-domain tracking, so you can track visits between domains that you own.
-
Infinitely scalable for businesses of any size.
-
Ongoing technical support from Google with a community of knowledgeable, supportive users.
There Are a Few Cons
- Difficult to customize advanced features.
- Keyword data lacks precision when attached to Google Search Console.
- The UI and platform isn’t intuitive, so novice users may find it hard to navigate.
- Terminology within Google Analytics is difficult to learn.
How Much Does Google Analytics Cost?
Once more with feeling, this beauty of a tool is totally free.
2. Google Search Console
Ah, Google Search Console -- your very own dashboard into the search engine itself.
GSC is your frontline of defense and where data first gathers for your domain. Search Console was formerly known as Google Webmaster Tools, but that definition is still accurate.
GSC is a set of diagnostic tools that measures your site's technical SEO health. Think of GSC like a stethoscope -- want to check your SEO heartbeat? Dive into the Search Analytics report and check out the impression rate and clicks. If impressions take a dive, you can kiss your organic traffic goodbye.
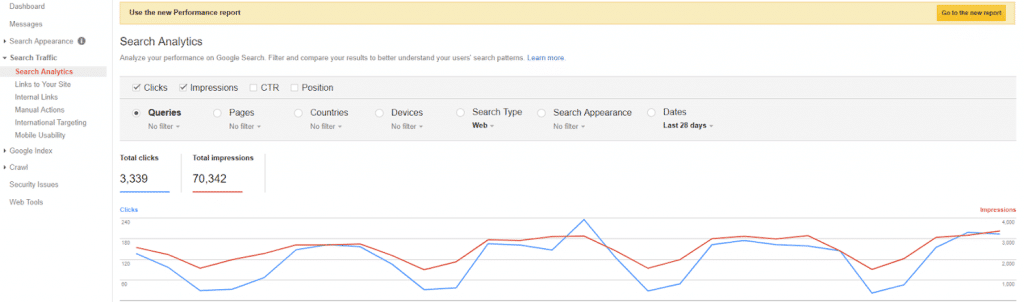
It's also the first place you should check if you suspect something happened to your traffic. It's a mandatory life-support tool for your website, at a price that won’t suffocate your wallet -- free!
Why It's Awesome
- Links clickstream data to Google Analytics -- impression, queries, click stats, etc.
- It’s Google's direct line to you for your website. Google notifies site owners about website and search issues through the messaging system within the Google Search Console.
- Customizable goals, views, and segments.
- Integrates with Google Tag Manager to track scroll depth, video metrics, button clicks, and much more.
- Cross domain-tracking -- as with Google Analytics, you can track visits between domains that you own.
- Infinitely scalable for organizations of any size.
- Solid support and knowledgeable community support.
There Are a Few Cons
- Difficult to customize advanced features.
- As with Google Analytics, it's not exactly intuitive to use for novice users.
- Also, the terminology is difficult to pick up, but be patient with yourself; it will start to make sense.
How Much Does Google Search Console Cost?
Swoon, also free.
(Psst! Here are our four favorite SEO improvements you can implement right now in Google Search Console.)
3. SEMrush
SEMrush is the digital marketer's (and SEO specialist's) Swiss Army Knife of reporting tools. It can handle SEO, PPC, social media, content, and public relations campaigns. Basically, it's a full-stack marketer's toolkit. If it can be tracked on the web, SEMrush has the data and it organizes it logically for you.
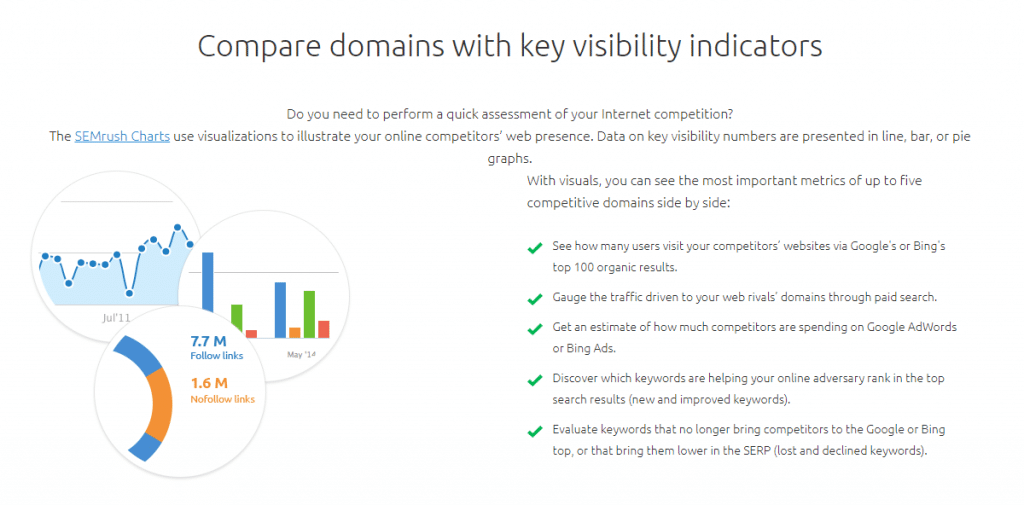
Need charts and graphs to build presentations with? Check.
Need to create automated weekly tracking for content performance? Check.
How about running a site audit for indexing issues, broken links, or missing titles? Yup. That too.
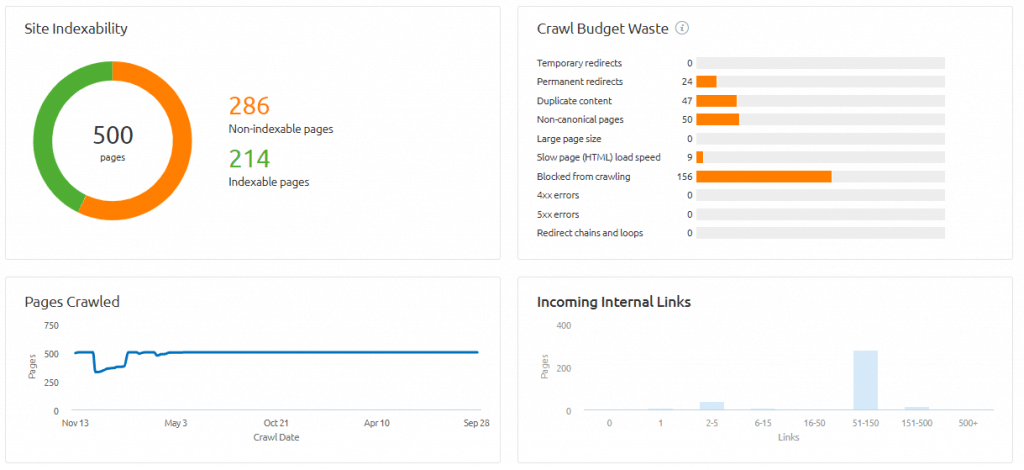
There’s not much SEMrush can’t do, and it does it all well. After you have Google Analytics and Google Search Console setup properly, SEMrush is the only other tool you need.
Why It's Awesome
- It's the de facto technical SEO tool.
- Robust domain and keyword analysis.
- Keyword position tracking tool.
- Competitive analysis for organic and paid keywords.
- SERP extras analysis -- featured listings, knowledge graph, rich cards, etc.
- PPC ad tracking.
- Exceptional reporting tool.
- White-label and custom reports, which can import data from Google Analytics, Search Console, and others.
- Organic traffic insights, including keywords by page with page views and session metrics.
- Content strategy analysis tools.
- Rich educational content with webinars and certification courses.
- One-click “Send to Trello” for site audit issues.
- Historical data with Guru level or above account.
There Are a Few Cons
- Steep learning curve for non-SEO specialists.
- Site audit tool is buggy at times when crawling sites not built on a standard CMS -- for instance, HubSpot COS and Kentico.
- Page response code reports (crawlability, performance) will render incorrect data if settings aren’t tweaked correctly.
- Organic traffic insights report limited to 50 results on Guru or lower plan.
- Organic traffic report not as precise as Google analytics, but does show decent trend data.
One Quick Note
SEMrush webinars and training are gold. The topics focus on a wide range of actionable marketing and SEO techniques, led by the internet's leading digital marketers and technologists.
How Much Does SEMrush Cost?
SEMrush is definitely a freemium product, with plans (beyond free) that start at $99 per month and go up to $399+ per month.
4. Screaming Frog
Respect the frog. When Google Search Console data lets you down and you need to crawl a site for broken links or missing on-page features, fire up Screaming Frog.
It’s a site crawler that logs the response codes it receives from the server. In a nutshell, it’s like Google’s spider that you control.
When the results are in, you can slice and dice the data and export a task list to Excel or Trello. Brilliant.
In the latest version, they added visualizations. (They finally listened to me! 😀) What does this super-power allow an SEO to do? Check this out:
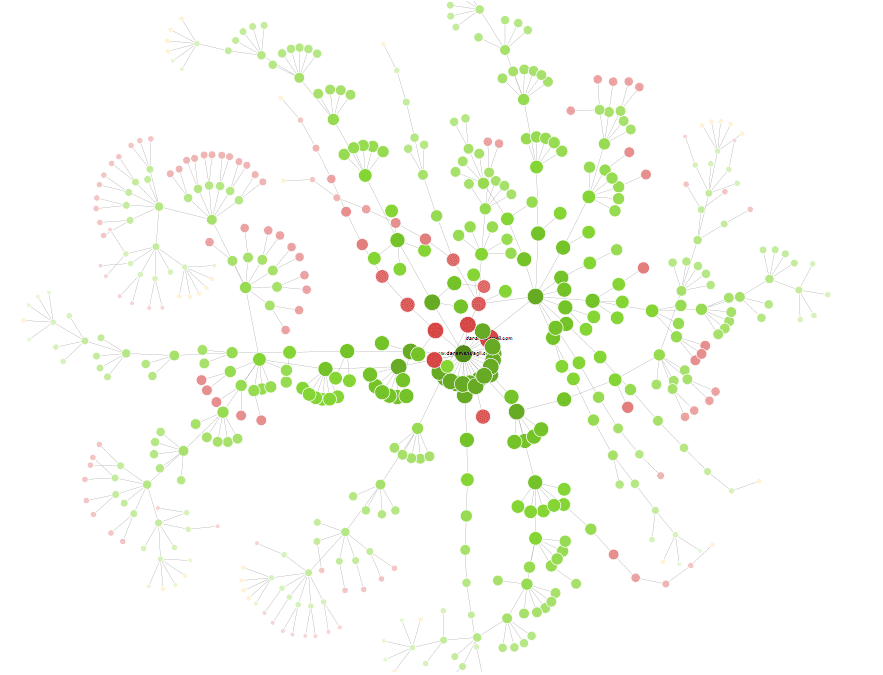
Isn't it beautiful? Each dot represents a page of your site. The branches show navigational structure and internal relationships for groups of pages like content pillars.
The red dots are broken links and the pink dots are redirects. Need to clean up your navigational structure? Grab a license and audit your site like the pros do.
The free version limits the crawl to 500 URLs, with no integration to Google Analytics or Search Console. However, the paid version is a fabulous tool for owners of larger sites.
Why It's Awesome
- Crawl a site like Google-bot does.
- Get a holistic picture of your website from a computer's point of view.
- Discover nonindexable paths, broken links, and redirects instantly.
- Extract data to Excel for further insight.
- Integrate Google Analytics and Search Console to view impression, clicks, and page views by URL.
- Get complete lists of on-page errors like missing meta-descriptions, H1s, titles, and redirects in one simple report
- New visualizations tool gives you a bird’s eye view of the directory tree, so you can instantly spot 404s (broken links) and content that can't be indexed.
- Save crawls to local or cloud drives.
- Run scheduled crawls for ongoing site maintenance.
There Are a Few Cons
- Made for technical SEO specialists, so the learning curve is steep for those new to the field.
- Tweaking the configuration takes knowledge of servers and platforms.
- Memory settings need adjustment if you’re crawling large sites -- 10,000 URLs or more.
How Much Does Screaming Frog Cost?
This bad boy is another freemium product, with perks for those willing to spend £99.00 per year.
Chapter 10: What Is the Future of SEO?
Let's peer into our crystal ball and see what SEO reincarnation looks like. We talked a little bit about voice search. Voice search -- given the current statistics, and the fact that it's extremely convenient -- looks like it's here to stay.
Google has said that their goal is to make Google behave like the computer from Star Trek, available to answer a question on any topic within milliseconds for any subject in the history of mankind -- kind of like my 12-year-old son...

Is this my son or a futuristic Google supercomputer? You decide.
When we peer into this amazing future, we see that our lives will be even more convenient by not having to interact physically with a screen or keyboard to get the precise answer we want instantly.
And when we account for all of the new rich-listing features that Google recommends -- local pack entries, maps, knowledge panel, Google My Business, and other structured data -- we start to understand that Google wants to help search results become more useful to users.
If a digital marketer can leverage these tools to make their search queries more feature rich, then they'll win a bigger share of the organic traffic. Assuming there’s any left.
Another challenge on our way to this bright future is web speed. The more features that we add to a website, the slower it gets. The web speed community agonizes between adding user interface elements, and reducing the page size so the browsers start rendering a page in one second or less.
Yes, you read that right. Google wants developers to target one second as an acceptable load time for your webpage. Does that give you a sense of how real this struggle is?
Removing excessive -- and, frankly, unnecessary features -- like image sliders and client-side rendered JavaScript will be the future of SEO. Remember, Star Trek computer speed.
So, in the future, we may very well be reflecting on the death of SEO and heralding in a new era of a different kind of search. One that is much richer and user friendly.
From a marketer's perspective, it is exceedingly difficult. But changing our viewpoint from frustration to curiosity, we can keep SEO alive and productive until the day when machines kill us all.
